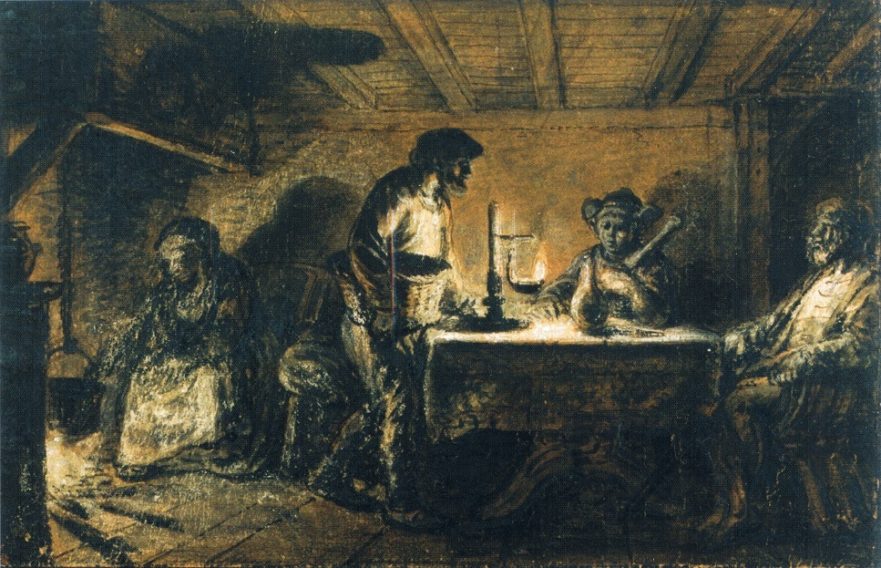
David N. Bivin and Joshua N. Tilton suggest a Hebrew reconstruction of Jesus’ instructions about how the twelve apostles were to behave when they entered a town. In this pericope we learn about the giving and receiving of hospitality among Jesus’ earliest followers. We also learn what may be wrong about the popular view that shaking the dust from the apostles’ feet was a symbolic action meant to signal to Jews who rejected Jesus that they were henceforth to be considered as Gentiles.
“Shake the Dust from Your Feet”: What Did the Apostles’ Action Signify?
The standard interpretation of the apostles’ dust-shaking action proposes that Jesus turned the concept of the impurity of Gentile lands against the Jewish inhabitants of cities within the (ritually pure) land of Israel. This interpretation concludes that shaking the dust from their feet dramatically symbolized that Jesus’ apostles would henceforth regard the Jewish inhabitants of a city that had rejected their message as though they were cut off from Israel. It is time for this mistaken interpretation to finally be put to rest.
Jesus’ Attitude Toward the Samaritans
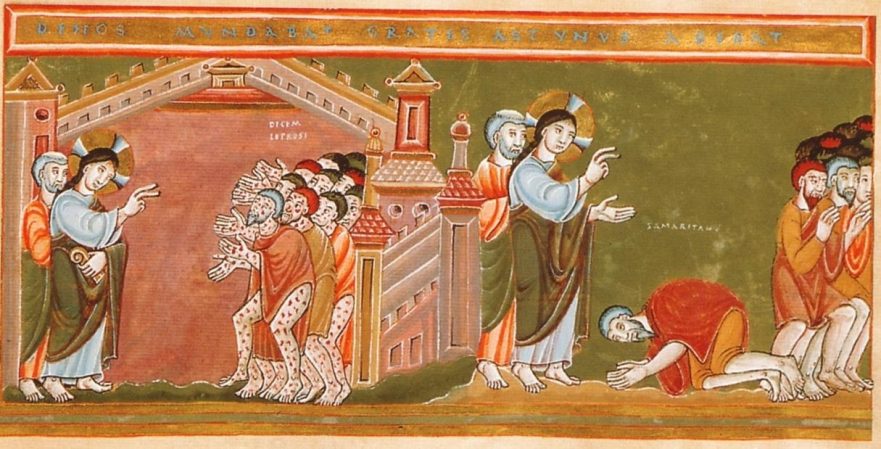

It is always our duty to ask ourselves whether the kind of speech we voice and the kind of rhetoric we listen to engenders respect for our neighbor, no matter how different she or he might be from ourselves, or whether it is sowing the seeds of hatred and violence.
Sending the Twelve: Conduct on the Road

In this segment of the LOY commentary David Bivin and Joshua Tilton consider the command to avoid Gentiles and Samaritans and the prohibitions against bringing travel gear for the apostles’ journey.
A Statistical Approach to the Synoptic Problem: Part 3—Single Tradition

In Part Three of his series, “A Statistical Approach to the Synoptic Problem,” Halvor Ronning examines the data concerning the degree to which each of the Synoptic Gospels was influenced by a Semitic language (Hebrew or Aramaic). Ronning analyzes this data to see whether it can help us unravel the vexed question: “Who wrote first? Matthew, Mark, or Luke?”
The Good Samaritan

The parable of the Good Samaritan came as a response to the lawyer’s question, “And who is my neighbor?” The lawyer wanted Jesus to draw a circle defining who is inside, and therefore the neighbor I must love, and who is outside. Jesus, by using Leviticus 19:34, ingeniously turned the lawyer’s question on its head.
This article is a sample chapter of Marc Turnage’s, Windows into the Bible: Cultural and Historical Insights into the Bible for Modern Readers (Springfield, Mo.: Logion, 2016), which will be released at the end of March 2016.
The Census of Quirinius and Luke 2

Modern readers tend to overlook the significance of the date of Quirinius’ census in the Infancy Narrative of Luke’s Gospel.
Parables on the Character of God

Jerusalem Perspective is excited to announce that in the coming months Dr. R. Steven Notley will be sharing a series of blogs on Jesus’ parables with our readers. In anticipation of these blogs, and as a preview of what we might expect from Dr. Notley, we are sharing two sermons on the parables that Dr. Notley delivered to the Narkis Street Congregation in Jerusalem. Enjoy!
A Statistical Approach to the Synoptic Problem: Part 2—Double Tradition

In the previous article of this series Halvor Ronning examined the statistics of verbal identities involved in comparisons between materials shared by all three Synoptic Gospels (Triple Tradition). Now in Part Two Ronning will bring into consideration the statistics pertaining to materials shared in only two Synoptic Gospels (Double Tradition). Ronning wiargues that the consistency with which an author treats his sources is a major clue for determining the order of Synoptic dependence.
Feast of the Circumcision (New Year’s Day)
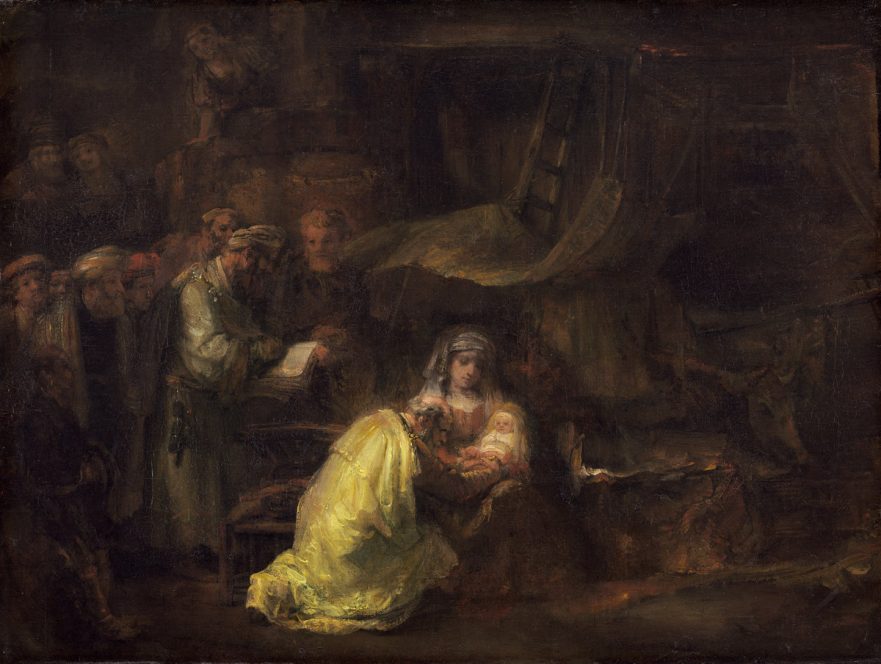

The first of January, celebrated around the world as New Year’s Day, is also the eighth day of Christmas and, as such, the Feast of the Circumcision and Naming of Jesus. Of course, no one knows on what day of the year Jesus was actually born, but since it has become traditional to celebrate Jesus’ birth on the 25th of December, it follows that the first of January is the day on which Christians celebrate the circumcision and naming of Jesus.
A Statistical Approach to the Synoptic Problem: Part 1—Triple Tradition

“A Statistical Approach to the Synoptic Problem,” a new series on Jerusalem Perspective by Jerusalem School of Synoptic Research member Halvor Ronning, aims to contribute to the body of empirical data that must be accounted for by any viable theory that attempts to describe the interrelationships between the Synoptic Gospels. To that end, Halvor Ronning has developed and adapted several new methods of quantifying and testing synoptic hypotheses which will be described and applied in “A Statistical Approach to to the Synoptic Problem.”
Matthew 1:1-25: In the Year of Jubilee?

The genealogies of Matthew and Luke reflect diverging Jewish opinions about the time for the advent of the redeemer.
Sending the Twelve: “The Harvest Is Plentiful” and “A Flock Among Wolves”
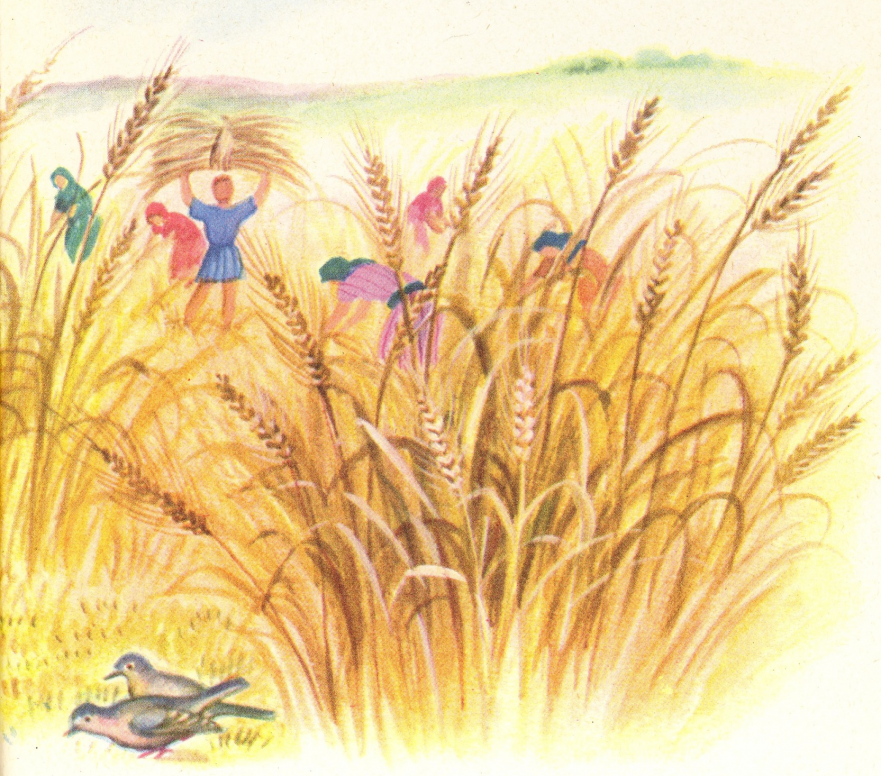

Yeshua told his twelve emissaries: “There’s a huge harvest, but a shortage of harvesters. So send word to the owner of the field to hire more workers to help them finish the job.
“Go! But beware, I’m sending you out like a defenseless flock into a pack of ravenous wolves.”
Sending the Twelve: Commissioning

Yeshua summoned his twelve emissaries to Israel and he gave them power to drive out dangerous spirits and to heal every disease and sickness those spirits had caused. Then he sent them on ahead in pairs to every city he intended to visit.
Choosing the Twelve

One day Yeshua called his disciples together and chose twelve of them to be his emissaries to Israel. Their names were Shimon Petros and Andrai (his brother), Yaakov, Yohanan, Pelipah, Talmai’s son, Matai, Tomah, Yaakov Halfi’s son, zealous Shimon, Yehudah Yaakov’s son, and Yehudah from Keriyot, who was a traitor.
The Origin of the Gospels

The July issue of The Church Quarterly Review in 1922 contained an article by William Lockton in which the author challenged the scholarly consensus concerning the solution to the Synoptic Problem. This important study, which is now in the public domain, was later to be of great importance to Rev. Dr. Robert L. Lindsey as further confirmation of Lindsey’s growing conviction that the Gospel of Mark is a highly edited epitome of the Gospel of Luke.
Character Profile: Chief Priests and Sadducees

Why did the chief priests and Sadducees continue to oppose the early believers even after the crucifixion of Jesus? In this video Marc Turnage places the chief priests and Sadducees in their historical context and explains why the preaching of the apostles was unwelcome news to the Temple authorities in Jerusalem.
The Messianic Consciousness of Jesus: Lesson 01

In Lesson One of The Messianic Consciousness of Jesus series, Dr. Robert L. Lindsey examines the story of the youthful Jesus asking and answering questions in the Temple.

