In this article, we will discuss the second type of parallelism: Antithetical Parallelism.
Cataloging the Gospels’ Hebraisms: Part Five (Parallelism)

Parallelism is a central feature of Hebrew poetry. It permeates the words of biblical poet and prophet. The frequency with which parallelism occurs in the utterances of Jesus is surprising, and leads inevitably to the conclusion that the Greek source (or, sources) used by the authors of Matthew, Mark and Luke derive(s) from a Greek translation (or, translations) of Hebrew documents.
Cataloging the Gospels’ Hebraisms: Part Four (Parallelism)

Doubling, or repeating, is a characteristic feature of Hebrew. Hebrew loves to say things twice (or more!) by adding equivalents. Words, phrases, sentences, and even stories, are doubled (or tripled).
Cataloging the Gospels’ Hebraisms: Part Three (Impersonal “They”)

Awareness of even the simplest Hebrew grammatical structure can bring to life a vague, or difficult-to-understand, saying of Jesus. Since potential Hebrew idioms are so dense in the Greek texts of Matthew, Mark and Luke, one has to ask, Could these apparent Hebrew idioms be evidence that the synoptic Gospels are descendants of an ancient translation of a Hebrew “Life of Jesus,” the gospel that the church father Papias spoke of when he wrote: “Matthew…arranged the sayings [of Jesus] in the Hebrew language”?
Cataloging the Gospels’ Hebraisms: Part Two (Luke 9:51-56)

Relatively few of the suggested Semitisms underlying the Greek New Testament constitute clear-cut proof for a Hebrew undertext, but a high density of Hebraisms in a given passage increases the probability that it is “translation Greek.”
Jesus and the Enigmatic “Green Tree”

Jesus made bold messianic claims when he spoke. To thoroughly understand these claims, however, we must get into a time machine and travel back in time to a completely different culture, the Jewish culture of first-century Israel. We must acculturate ourselves to the way teachers and disciples in the time of Jesus communicated through allusions to Scripture.
The Value of Rabbinic Literature as an Historical Source

The thesis of this article is that rabbinic sources, when used in a careful manner, can provide reliable historical material pertaining to the Second Temple period. If this thesis is accepted, the consequences for the study of the New Testament Gospels are obvious.
Why Learn to Speak a Dead Language?
Why would anyone in his or her right mind want to speak a “dead” language, a language that no one speaks? The answer: Because only by speaking a language does one internalize it, and it was high time, Randall and I felt, having tasted fluency in Hebrew, that we should gain an active knowledge of Koine Greek.
What’s Happening to the Holy Tongue?
English speakers who live in Israel are reminded regularly of the inroads English is making in Hebrew.
Hebrew or Aramaic? Some Evidence from Inscriptions
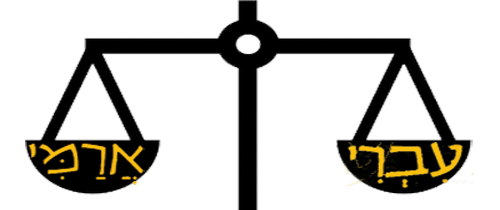
The fundamental assumptions of the past of Jesus’ mother tongue are again and again repeated today while their frame of reference has changed dramatically.
